-
1 tensor in n dimensions
1) Математика: n-мерный тензор2) Макаров: тензор n-го рангаУниверсальный англо-русский словарь > tensor in n dimensions
-
2 tensor
-
3 dimensions
размер, размеры -
4 dimension
-
5 dimension d'une grandeur, f
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:
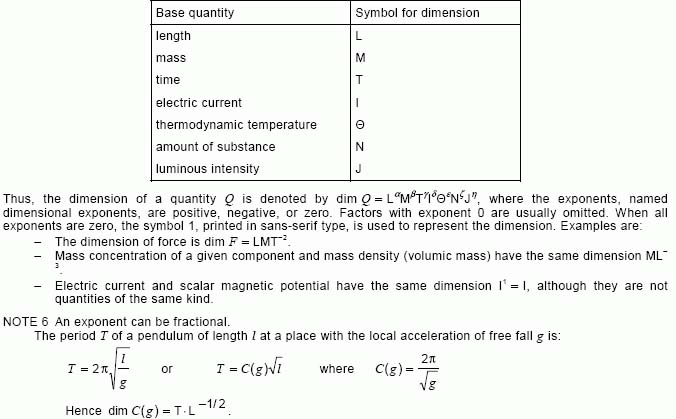
[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > dimension d'une grandeur, f
-
6 dimension, f
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > dimension, f
-
7 Dimension einer Grösse
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dimension einer Grösse
-
8 Dimension, f
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dimension, f
-
9 Größendimension, f
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Größendimension, f
-
10 dimension
- устанавливать размеры
- размерность физической величины
- размерность (величины)
- размерность (векторного пространства)
- размерность
- размер
- протяжённость (во времени)
- мн. габариты
- габариты (мн.)
габариты (мн.)
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
мн. габариты
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
протяжённость (во времени)
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
размер
Значение линейной, угловой или какой-либо другой величины в принятых единицах измерения
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
DE
FR
размерность
—
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
размерность (векторного пространства)
—
[http://www.rfcmd.ru/glossword/1.8/index.php?a=index&d=23]Тематики
EN
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
устанавливать размеры
задавать размеры
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > dimension
-
11 dimension of a quantity
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных величин в различных степенях, отражающее связь данной величины с основными величинами и имеющее коэффициент пропорциональности, равный 1 (ОСТ 45.159-2000.1 Термины и определения (Минсвязи России)).
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > dimension of a quantity
-
12 quantity dimension
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > quantity dimension
См. также в других словарях:
Tensor — For other uses, see Tensor (disambiguation). Note that in common usage, the term tensor is also used to refer to a tensor field. Stress, a second order tensor. The tensor s components, in a three dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, form the… … Wikipedia
Tensor product — In mathematics, the tensor product, denoted by otimes, may be applied in different contexts to vectors, matrices, tensors, vector spaces, algebras, topological vector spaces, and modules. In each case the significance of the symbol is the same:… … Wikipedia
Tensor product of fields — In abstract algebra, the theory of fields lacks a direct product: the direct product of two fields, considered as a ring is never itself a field. On the other hand it is often required to join two fields K and L, either in cases where K and L are … Wikipedia
tensor — noun Etymology: New Latin, from Latin tendere Date: circa 1704 1. a muscle that stretches a part 2. a generalized vector with more than three components each of which is a function of the coordinates of an arbitrary point in space of an… … New Collegiate Dictionary
Weyl tensor — In differential geometry, the Weyl curvature tensor, named after Hermann Weyl, is a measure of the curvature of spacetime or, more generally, a pseudo Riemannian manifold. Like the Riemann curvature tensor, the Weyl tensor expresses the tidal… … Wikipedia
Dyadic tensor — In multilinear algebra, a dyadic is a second rank tensor written in a special notation, formed by juxtaposing pairs of vectors, along with a notation for manipulating such expressions analogous to the rules for matrix algebra. Each component of a … Wikipedia
Einstein tensor — The Einstein tensor expresses spacetime curvature in the Einstein field equations for gravitation in the theory of general relativity. It is sometimes called the trace reversed Ricci tensor. Definition In physics and differential geometry, the… … Wikipedia
Cotton tensor — In differential geometry, the Cotton tensor on a (pseudo) Riemannian manifold of dimension n is a third order tensor concomitant of the metric, like the Weyl tensor. The concept is named after Émile Cotton. Just as the vanishing of the Weyl… … Wikipedia
Metric tensor (general relativity) — This article is about metrics in general relativity. For a discussion of metrics in general, see metric tensor. Metric tensor of spacetime in general relativity written as a matrix. In general relativity, the metric tensor (or simply, the metric) … Wikipedia
Scalar-tensor theory — Scalar tensor theories are theories that include a scalar field as well as a tensor field to represent an interaction, especially the gravitational one. Tensor fields and field theory Modern physics tries to derive all physical theories from as… … Wikipedia
Lanczos tensor — There are two different tensors sometime referred to as the Lanczos tensor (both named after Cornelius Lanczos):* A tensor in the theory of quadratic Lagrangians, which vanishes in four dimensions. * The potential tensor H for the Weyl tensor C … Wikipedia
